MATERIAL AND METHODS
All chemicals and reagents were procured from Merck India limited. The standard bacterial and fungal stains were procured from National Centre for Cell Science, Pune, India. Melting points were determined using X-6 digital display binocular microscope. Infrared spectra were taken on a nicolet nexus 470 FT-IR spectrometer using smear KBr crystals. NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance (300 MHz) spectrometer. All molecules were docked into binding pocket by using Grid-based Ligand Docking with Energetics (GLIDE) module of Schrodinger. A total of 10 ligand conformations were allowed and finally top score conformation was selected as active conformation. Molecules were analyzed based on docking score, interacting amino acids and hydrogen bonds.
The synthesized ligands were sketched and geometry was optimized using Maestro workspace of Schrodinger Suite 2012. Ligands for docking were prepared by using Ligprep, a versatile program to generate three dimensional module of Schrodinger and minimized using OPLS-2005 force field. Crystal coordinates of E. coli beta-ketoacyl-acp synthase III (FabH) were taken from PDB ID 1HNJ. Protein for docking studies was prepared using protein preparation wizard of Schrodinger (Maestro, v9.3 Schrodinger, LLC, New York, NY). Bond orders and formal charges were added for hetero groups and hydrogens were added to all atoms in the system. Water molecules with in 5A0 distance were removed. Glide energy grid with coordinates of X: 28.56; Y: 8.86; Z: 33.83 around malonyl-coA binding site were generated for the prepared protein.
Synthesis of title compounds (7a-7e)
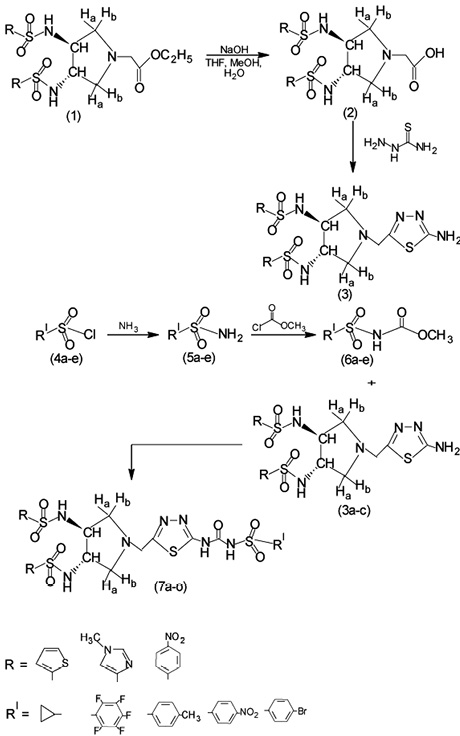
Ethyl 2-((3S, 4S)-3, 4-disubstituted-sulfonamido)pyrrolidinyl-N-acetate derivatives (1a-1c) were synthesized by the procedure reported in the literature (Santosh, Raveendra, Madhu & Ravindranath, 2012).
Synthesis of [3, 4-Bis-(thiophene-2-sulfonylamino)-pyrrolidin-1-yl]-acetic acid (2a)
An arqueous solution of NaOH (2N, 30 mL) was added to the solution of ester 1a (5 mmol, 2.398 g) in tetrahydrofuran / MeOH / H20 (1:1:1) and stirred at room temp. The excess of solvent was evaporated under vacuum to give crude residue. The residue was washed with EtOAc, acidified with 1N HCl to a pH 2 and was filtered under vacuum to get fine solid. In case a solid is not obtained, the solution was extracted with two 100 mL portions of EtOAc. The organic layer was collected, washed with water, brine, dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and evaporated under vacuum to give crude acid product. The crude product was purified by column chromatography (60 mesh-silica gel -120 mesh-silica gel, Eluent: 70% EtOAc-30% petroleum ether). Similar procedure was followed for the synthesis of other compounds of the series.
Synthesis of N,N'-((3S, 4S)-1-((5-amino-1, 3, 4-thiadiazol-2-yl)methyl) pyrrolidine-3, 4-diyl)bis(thiophene-2-sulfonamide) (3a)
Concentrated H2SO4 (12 mL) was added slowly to a mixture of carboxylic acid 2a (10 mmol, 4.515 g) and thiosemicarbazide (12 mmol, 1.093 g) in a three necked round bottom flask fitted with a reflux condenser. The reaction mixture was refluxed on a water bath for 3 h, poured into crushed ice and neutralized with ammonia solution. The yellow colored solid separated was filtered, washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution and water, dried and recrystallized from ethanol. Similar procedure was adopted for the synthesis of other compounds (3b & 3c) of the series.
Synthesis of Cyclopropanesulfonyl chloride (5a)
A mixture of cyclopropanesulfonylchloride (10 mmol, 1.906 g) and 20% aqueous ammonia solution was taken in a four necked round bottom flask fitted with a reflux condenser. The reaction mixture was heated at 75 ºC - 80 ºC for 3 h. The reaction mixture was allowed to stand for 1 h at 15 ºC, the solid that separated was filtered, washed with large quantity of water and dried to get 4-methyl benzenesulfonamide. Similar procedure was adopted for the synthesis of other compounds (5a-5e) of the series.
Synthesis of methyl cyclopropylsulfonylcarbamate (6a)
A mixture of cyclopropanesulfonylchloride (10 mmol, 1.21 g), ethyl methyl ketone (8 mL) and potassium carbonate was taken in a four necked round bottom flask and heated to 80 ºC for 30 min. Methyl chloroformate (10 mL) was added drop wise at 45 ºC. The mixture was heated for 8 h at 50 ºC. After the completion of reaction (monitored by TLC), the reaction mixture was poured into ice cold water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The pH of the aqueous layer was adjusted to a 2.5 by the addition of hydrochloric acid and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and the solution was concentrated to dryness. The solid thus obtained was recrystallized from ethanol. Similar procedure was adopted for the synthesis of other compounds (6b-6e) of the series.
Synthesis of N,N'-((3S, 4S)-1-((5-(3-(cyclopropylsulfonyl)ureido)-1, 3, 4-thiadiazol-2-yl)methyl)pyrrolidine-3, 4-diyl)bis(thiophene-2-sulfonamide) (7a)
A mixture of 6a (10 mmol, 1.409 g) and amine 3a (10 mmol, 1.79 g) in toluene (50 mL) was taken in a three necked round bottom flask fitted with a reflux condenser and a mechanical stirrer. The reaction mixture was refluxed for 4 h, cooled to room temperature, resulting solid was filtered, dried and recrystallized from methanol to obtain 7a. Similar procedure was adopted for the synthesis of other compounds (7b-7o) of the series. The sequence of reactions is given in the scheme 1.
|
| |
 |
| |
Scheme 1. Synthesis of title compounds 7(a-7o).
Source: Authors own elaboration. |
 |
Scheme 1. Synthesis of title compounds 7(a-7o).
Source: Authors own elaboration. Close |
Characterization of compounds 2(a-c)
Compound; R; Molecular formula; Yield (%); m.p. (ºC); Element Found% (calculated%); IR (Group)νmax in cm–1; 1H NMR (300MHz, DMSO-D6) δ ppm.
2a: Thiophene; C14H17N3O6S4;76;191-3; C 37.21 (37.24), H 3.77 (3.79), N 9.33 (9.31); (C-N Cyclic)1100, (C-N exo)1117, (O = S = O)1320 and 1185, (C-N imidazole)1550, (C = N)1615, (C = O Acid)1755, (N-H) 3210; 7.65-7.22 (m, 6H, of thiophene), 7.47 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 4.22(s,1H, -COOH), 3.50 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 3.25 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-CO), 2.88(m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.29 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
2b: 1-Methyl-1H-imidazole; C14H21N7O6S2;71;197-9; C 37.55 (37.58), 4.69 (4.73), N 21.89 (21.91); (C-N Cyclic)1116, (C-N exo)1120, (O = S = O)1326 and 1186, (C-N imidazole)1559, (C = N)1617, (C = O Acid)1757, (N-H) 3215; 7.90 (2H, -N-CH-N- of imidazole), 7.47 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 6.93 (s, 2H, N-CH- of two imidazole), 4.22 (s, 1H, -COOH), 3.65 (s, 6H, N- CH3 of imidazole), 3.50 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 3.25 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-CO-), 2.88(m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.29 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
2c: p-Nitro phenyl; C18H19N5O10S2;82;182-4; C 40.81 (40.83), H 3.63 (3.62), N 13.28 (13.23); (C-N Cyclic)1122, (C-N exo)1125, (O = S = O)1323 and 1189, (C-N imidazole)1557, (C = N)1619, (C = O Acid)1762, (N-H) 3217; 8.12-8.39 (m, 8H, aromatic protons), 7.47 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 4.22 (s, 1H, -COOH), 3.50 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 3.25 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-CO-), 2.88(m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.29 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
Characterization of compounds 3(a-c)
Compound; R; Molecular formula; Yield (%); m.p. (ºC); Element Found% (calculated%); IR (Group)νmax in cm–1; 1H NMR (300MHz, DMSO-D6) δ ppm.
3a: Thiophene; C15H18N6O4S5;79;197-9; C 35.55 (35.56), H 3.52 (3.58), N 16.53 (16.59); (C-S-C thiadiazole) 695, (O = S = O)1323 and 1185, (C = N thiadiazole)1670, (-NH2)3356 and 3263, (NH sulphonamide)3421; 7.65-7.22 (m, 6H, of thiophene), 7.47 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 3.62 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.33 (s, 2H, -NH2), 3.11 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.61(m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.55 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
3b: 1-Methyl-1H-imidazole; C15H22N10O4S3;68;202-4; C 35.81 (35.85), H 4.44 (4.41), N 27.82 (27.87); (C-S-C thiadiazole)705, (O = S = O)1326 and 1187, (C = N thiadiazole)1673, (-NH2)3359 and 3268, (NH sulphonamide)3420; 7.90(2H, -N-CH-N- of imidazole), 7.47 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 6.93 (s, 2H, N-CH- of two imidazole), 3.65 (s, 6H, N- CH3 of imidazole), 3.59 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.35 (s, 2H, -NH2), 3.17 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.88(m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.52 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
3c: p-Nitro phenyl; C19H20N8O8S3;73;192-4; C 39.09 (39.04), H 3.42 (3.45), N 19.15 (19.17); (C-S-C thiadiazole)728, (O = S = O)1337 and 1199, (-NH2)3367 and 3279, (C = N thiadiazole)1680, (NH sulphonamide)3422; 8.12-8.39 (m, 8H, aromatic protons), 7.47 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 3.69 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.50 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 3.39 (s, 2H, -NH2), 2.97(m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.33 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
Characterization of compounds 6(a-e)
Compound; R; Molecular formula; Yield (%); m.p. (ºC); Element Found% (calculated%); IR (Group)νmax in cm–1; 1H NMR (300MHz, DMSO-D6) δ ppm.
6a: Cyclopropyl; C5H9NO4S;61;205-7; C 33.53 (33.51), H 5.09 (5.06), N 7.81 (7.82); (C-O)1254, (-CH3)1342 and 1265, (C = O)1640, (-CH3)2915 and 2875, (N-H)3212; 9.22 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 3.67 (s, 3H, -OCOCH3), 1.75(m, 1H, -SO2-CH), 0.79(m, 4H, cyclopropyl -CH2-).
6b: Pentafluorophenyl; C8H4F5NO4S; 59; 186-8; C 31.45(31.48), H 1.35 (1.32), N 4.52 (4.59); (C-O)1269, (-CH3)1358 and 1279, (C = O)1648, (-CH3)2915 and 2875, (N-H)3215; 9.22 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 3.69 (s, 3H, -OCOCH3).
6c: p-Tolyl; C9H11NO4S;69;192-4; C 47.19 (47.15), H 4.83 (4.84), N 6.15 (6.11); (C-O)1257, (-CH3)1347 and 1264, (C = O)1650, (-CH3)2915 and 2875, (N-H)3214; 8.86 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 7.83 (d, 2H, Ar-H meta to methyl), 7.34 (d, 2H, Ar-H ortho to methyl), 3.57 (s, 3H, -OCOCH3).
6d: p-Bromo phenyl; C8H8BrNO4S;62;180-2; C 32.67 (32.67), H 2.77 (2.74), N 4.73 (4.76); (C-O)1259, (-CH3)1349 and 1268, (C = O)1654, (-CH3)2915 and 2875, (N-H)3203; 8.89 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 7.87 (d, 2H, Ar-H meta to bromo), 7.77 (d, 2H, Ar-H ortho to bromo), 3.59(s, 3H, -OCOCH3).
6e: p-Nitro phenyl; C8H8N2O6S;67;196-8; C 36.89 (36.92), H 3.12 (3.10), N 10.73 (10.77); (C-O)1263, (-CH3)1352 and 1273, (C = O)1666, (-CH3)2915 and 2875, (N-H)3217; 8.97(s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 8.49 (d, 2H, Ar-H ortho to nitro), 8.21 (d, 2H, Ar-H meta to nitro), 3.65(s, 3H, -OCOCH3).
6e: p-Nitro phenyl; C8H8N2O6S;67;196-8; C 36.89 (36.92), H 3.12 (3.10), N 10.73 (10.77); (C-O)1263, (-CH3)1352 and 1273, (C = O)1666, (-CH3)2915 and 2875, (N-H)3217; 8.97(s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 8.49 (d, 2H, Ar-H ortho to nitro), 8.21 (d, 2H, Ar-H meta to nitro), 3.65(s, 3H, -OCOCH3).
Characterization of compounds 7(a-o)
Compound; R; R1; Molecular formula; Yield (%); m.p. (ºC); Element Found% (calculated%); IR Groupνmax in cm–1; 1H NMR (300MHz, DMSO-D6) δ ppm; 13C-NMR (300MHz, DMSO-D6) (δ ppm).
7a: Thiophene; Cyclopropyl; C19H23N7O8S6;61;212-4; C 34.09 (34.07), H 3.43 (3.46), N 14.61 (14.64); (N-N)1052, (O = S = O)1362 and 1183, (C-N urea)1310, (C = O urea)1640, (NH sulphonamide)3319; 9.01 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 7.45-7.01 (m, 6H, of thiophene), 7.37 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 5.94 (s, 1H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.45 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.01 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.54(m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.35 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine), 1.54 (m, 1H, -SO2-CH), 0.67(m, 4H, cyclopropyl -CH2-); 62.3, 64.1, 137.2, 128.7, 132.6, 135.9,57.8, 64.1, 66.1, 157.5, 48.9, 12.5, corresponding to C2 and C2, C3 and C3,, C4 and C4,, C5 and C5,, C6 and C6,, C7 and C7,, C8, C9, C10,, C11,, C12,, C13 and C13, respectively.
7b: Thiophene; Pentafluorophenyl; C22H18F5N7O8S6; 59;192-4; C 33.22 (33.20), H 2.25 (2.28), N 12.29 (12.32); (N-N) 1033, (O = S = O)1352 and 1165, (C-N urea)1301, (C = O urea)1631, (NH sulphonamide)3311; 9.14 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 7.71-7.12 (m, 6H, of thiophene), 7.45 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 5.97 (s, 1H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.65 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.03 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.60 (m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.59 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
7c: Thiophene; p-Tolyl; C23H25N7O7S6;69;209-11; C 39.21 (39.25), H 3.56 (3.58), N 13.90 (13.93); (N-N) 1049, (O = S = O)1359 and 1179, (C-N urea)1308, (C = O urea)1641, (NH sulphonamide)3318; 8.86 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 7.83 (d, 2H, Ar-H meta to methyl), 7.62-7.24 (m, 6H, of thiophene), 7.32 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 7.34 (d, 2H, Ar-H ortho to methyl), 6.11 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.45 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.08 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.67(m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.51 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine), 1.90(s, 3H, -CH3, ArCH3).
7d: Thiophene; p-Bromo phenyl; C22H22BrN7O7S6; 68;201-3; C 34.33 (34.37), H 2.90 (2.88), N 12.74 (12.75); (N-N) 1045, (O = S = O)1357 and 1174, (C-N urea)1306, (C = O urea)1639, (NH sulphonamide)3316; 8.91 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 7.85 (d, 2H, Ar-H meta to bromo), 7.78 (d, 2H, Ar-H ortho to bromo), 7.41-7.16 (m, 6H, of thiophene), 7.44 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 5.71 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.67 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.15 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.66 (m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.71 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
7e: Thiophene; p-Nitro phenyl; C22H22N8O9S6;71; 189-91; C 35.16 (35.19), H 2.91 (2.95), N 14.89 (14.92); (N-N) 1040, (O = S = O)1354 and 1169, (C-N urea)1303, (C = O urea)1636, (NH sulphonamide)3313; 9.12 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 8.58 (d, 2H, Ar-H ortho to nitro), 8.28 (d, 2H, ArH meta to nitro), 7.50-7.01 (m, 6H, of thiophene), 7.52 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 6.27 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.69 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.18 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.71(m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.67 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
7f: 1-Methyl-1H-imidazole; Cyclopropyl; C19H27N11 O7S4; 67;209-11; C 35.11 (35.12), H 4.15 (4.19), N 23.69 (23.71); (N-N)1058, (O = S = O)1379 and 1189, (C-N urea)1316, (C = O urea)1642, (NH sulphonamide)3325; 9.25 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 7.91 (2H, -N-CH-N- of imidazole), 7.48 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 6.87 (s, 2H, N-CH- of two imidazole), 5.98 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.62 (s, 6H, N-CH3 of imidazole), 3.51 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.23 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.76 (m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.39 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine), 1.68(m, 1H, -SO2-CH), 0.65 (m, 4H, cyclopropyl -CH2-).
7g: 1-Methyl-1H-imidazole; Pentafluorophenyl; C22H38F5N11O7S4;58;198-200; C 37.15 (37.18), H 4.55 (4.56), N 18.31 (18.34); (N-N) 1035, (O = S = O)1359 and 1171, (C-N urea)1306, (C = O urea)1633, (NH sulphonamide)3316; 9.27 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 7.83 (2H, -N-CH-N- of imidazole), 7.41 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 6.81 (s, 2H, N-CH- of two imidazole), 6.10 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.65 (s, 6H, N-CH3 of imidazole), 3.53 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.15 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.83 (m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.47 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine); 62.7, 64.6, 143.2, 127.2, 122.8, 35.5, 58.8, 65.1, 66.9, 156.8, 125.1, 151.9, 139.1, 148.7 corresponding to C2 and C2, C3 and C3’, C4 and C4’, C5 and C5’, C6 and C6’, C7 and C7’, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13 and C13’, C14 and C14’, C15 respectively.
7h: 1-Methyl-1H-imidazole; p-Tolyl; C23H29N11O7 S4;59;201-3; C 39.45 (39.47), H 4.16 (4.18), N 22.00 (22.02); (N-N) 1055, (O = S = O)1376 and 1186, (C-N urea)1314, (C = O urea)1640, (NH sulphonamide)3323; 8.89 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 7.97 (2H, -N-CH-N- of imidazole), 7.84 (d, 2H, ArH meta to methyl), 7.58 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 7.39 (d, 2H, Ar-H ortho to methyl), 6.97 (s, 2H, N-CH- of two imidazole), 6.17 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.65 (s, 6H, N-CH3 of imidazole), 3.69 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.25 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.78(m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.45 (m, 2H, -CHb-protons of pyrrolidine).
7i: 1-Methyl-1H-imidazole; p-Bromo phenyl; C22H26 BrN11O7S4; 71; 199-201; C 34.51 (34.56), H 3.39 (3.43), N 21.11 (20.15); (N-N)1050, (O = S = O)1372 and 1183, (C-N urea)1313, (C = O urea)1638, (NH sulphonamide)3322; 8.97 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 7.89 (2H, -N-CH-N- of imidazole), 7.89 (d, 2H, Ar-H meta to bromo), 7.67 (d, 2H, Ar-H otho to bromo), 7.47 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 6.93 (s, 2H, N-CH- of two imidazole), 6.12 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.65 (s, 6H, N-CH3 of imidazole), 3.64 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.28 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.67(m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.54 (m,2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
7j: 1-Methyl-1H-imidazole; p-Nitro phenyl; C22H26 N12O9S4;70;207-9; 36.15 (36.16), H 3.55 (3.59), N 23.05 (23.00); (N-N)1046, (O = S = O)1365 and 1175, (C-N urea)1310, (C = O urea)1635, (NH sulphonamide)3319; 8.76 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 8.35 (d, 2H, Ar-H ortho to nitro), 8.02 (d, 2H, Ar-H meta to nitro), 7.91 (2H, -N-CH-N- of imidazole), 7.37 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 6.93 (s, 2H, N-CH- of two imidazole), 6.16 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.65 (s, 6H, N-CH3 of imidazole), 3.44 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.17 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.71 (m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.44 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
7k: p-Nitro phenyl; Cyclopropyl; C23H25N9O11S4; 69;202-4; C 37.71 (37.75), H 3.40 (3.44), N 15.19 (17.23); (N-N)1039, (O = S = O)1356 and 1165, (C-N urea)1321, (C = O urea)1645, (NH sulphonamide)3316; 9.21 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 8.14-8.38 (m, 8H, aromatic protons), 7.41 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 6.13 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.65 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.54 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.87(m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.37 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine), 1.71 (m, 1H, -SO2-CH), 0.74 (m, 4H, cyclopropyl -CH2-).
7l: p-Nitro phenyl; Pentafluorophenyl; C26H20F5N9 O11S4;61;204-6; C 36.38 (36.41), H 2.31 (2.35), N 14.68 (14.70); (N-N) 1025, (O = S = O)1339 and 1152, (C-N urea)1311, (C = O urea)1631, (NH sulphonamide)3309; 9.16 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 8.22-8.32 (m, 8H, aromatic protons), 7.48 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 6.13 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.70 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.51 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.87(m, 2H, -CHa-protons of pyrrolidine), 2.43 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
7m: p-Nitro phenyl; p-Tolyl; C27H27N9O11S4;62;212-4; C 41.46 (41.48), H 3.47 (3.48), N 16.09 (16.12); (N-N) 1035, (O = S = O)1353 and 1161, (C-N urea)1319, (C = O urea)1641, (NH sulphonamide) 3315; 8.94 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 8.19-8.32 (m, 8H, aromatic protons), 7.88 (d, 2H, Ar-H meta to methyl ), 7.43 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 7.34 (d, 2H, Ar-H ortho to methyl ), 6.16 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.67 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.63 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.96 (m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.45 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.06(s, 3H, -CH3, ArCH3).
7n: p-Nitro phenyl; p-Bromo phenyl; C26H24BrN9O11 S4;69;219-21; C 36.85 (36.88), H 2.83 (2.86), N 14.81 (14.89); (N-N) 1032, (O = S = O)1350 and 1158, (C-N urea)1317, (C = O urea)1638 (NH sulphonamide)3313; 8.92 (s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 8.12-8.39 (m, 8H, aromatic protons), 7.79 (d, 2H, Ar-H meta to bromo), 7.63 (d, 2H, Ar-H ortho to bromo), 7.45 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 6.16 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.75 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.50 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 3.01 (m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.36 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine).
7o: p-Nitro phenyl; p-Nitro phenyl; C26H24N10O13S4; 76; 206-8; C 38.41 (38.42), H 2.95 (2.98), N 17.19 (17.23); (N-N) 1028, (O = S = O)1344 and 1155, (C-N urea)1314, (C = O urea)1634, (NH sulphonamide)3311; 8.97(s, 1H, SO2-NH-), 8.51 (d, 2H, Ar-H ortho to nitro), 8.17-8.35 (m, 10H, aromatic protons), 7.47 (s, 2H, SO2-NH-), 6.02 (s, 2H, NH, D2O-exchange, disappear), 3.55 (s, 2H, -N-CH2-), 3.52 (m, 2H, -SO2-N-CH-), 2.92 (m, 2H, -CHa- protons of pyrrolidine), 2.29 (m, 2H, -CHb- protons of pyrrolidine); 62.4, 63.5, 146.2, 128.5, 124.1, 151.3, 65.0, 157.4, 59.1, 65.8, 65.1, 155.5, 147.8, 139.6, 136.5, 159.6 corresponding to C2 and C2’ C3 and C3’, C4 and C4’, C5 and C5’, C6 and C6’, C7 and C7’, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, C14, C15 and C15’, C16 and C16’, C17 respectively.